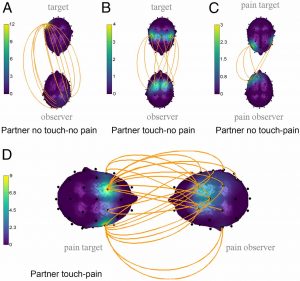
The mechanisms that underlie social touch analgesia are largely unknown. Here, we apply a hyperscanning approach with real-life interaction of dyads to examine the association between brain-to-brain coupling and pain relief. Our findings indicate that hand-holding during pain increases the brain-to-brain coupling network that correlates with the magnitude of the analgesia and the observer’s empathic accuracy. These findings make a unique contribution to our understanding of the physiological mechanisms of touch-related analgesia. Read full artice>>

